The 5-Layer Tech Stack: Career Options, Jobs, Skills & Real Examples for the Next 10 Years
Why do some people stay relevant for 20 years, while others struggle after just 3?
This is not about intelligence.
This is not about marks.
This is not about luck.
It is about understanding where you fit.
Every year, lakhs of students learn coding, AI, cloud, or data science.
Some grow fast.
Some get stuck.
Some quit tech completely.
The difference is simple.
Some people understand how technology is built.
Most people only see what is visible.
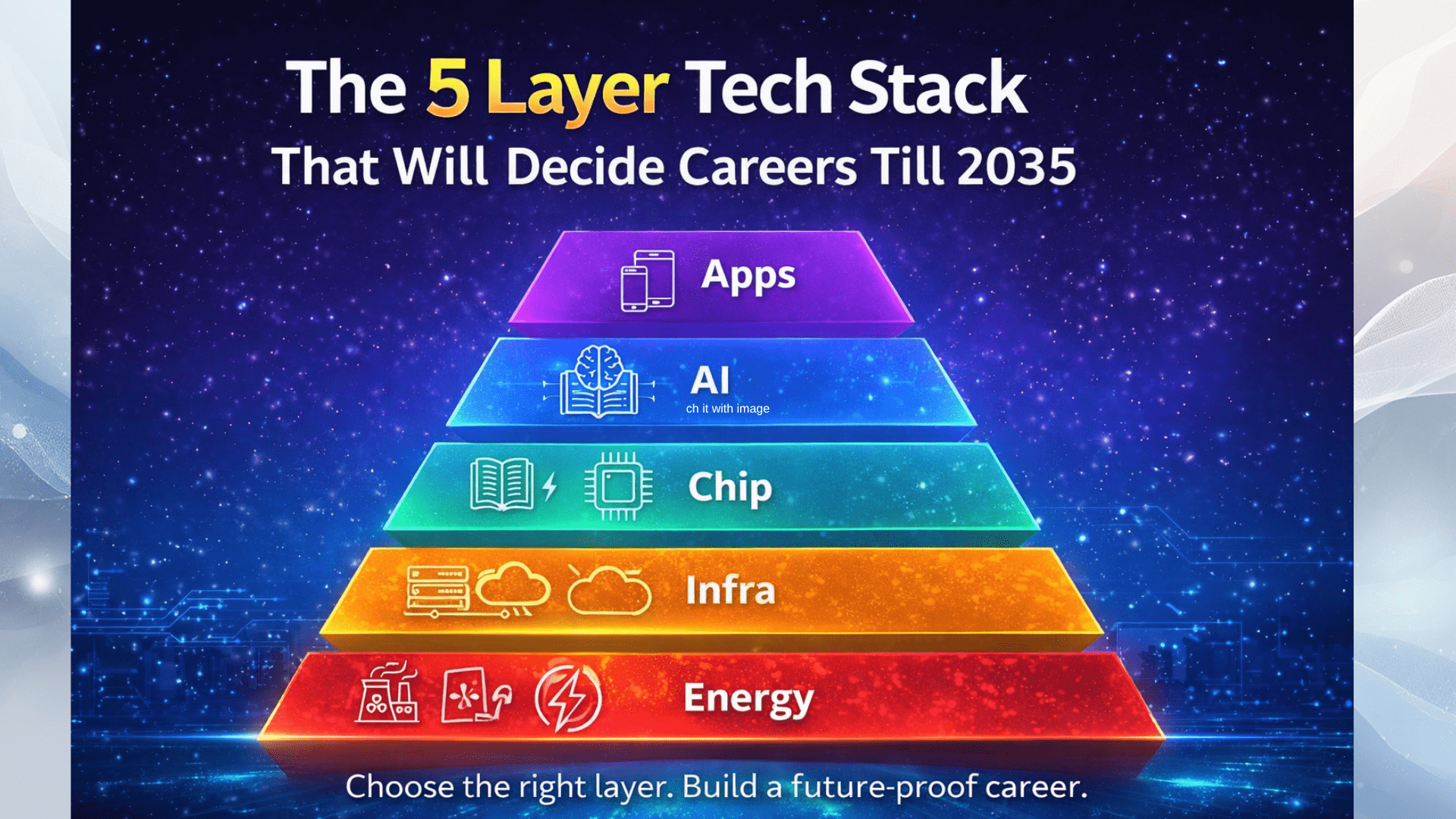
Behind every app, website, or AI tool, there is a 5-layer tech stack.
If you understand these layers early,
you stop chasing trends and start building a future-proof career.
A Reality Check You Should Not Ignore
Let us start with facts.
- Over 85 per cent of future jobs will require digital or technical skills
- AI is expected to create millions of new jobs, but also remove outdated ones
- Students who pick careers blindly struggle the most
This is why students keep searching:
- best tech careers for the next 10 years
- Future Skills for 2030
- AI career roadmap for students
But answers remain confusing.
Why?
Because most career advice talks about skills, not systems.
Technology is a system.
And systems have layers.
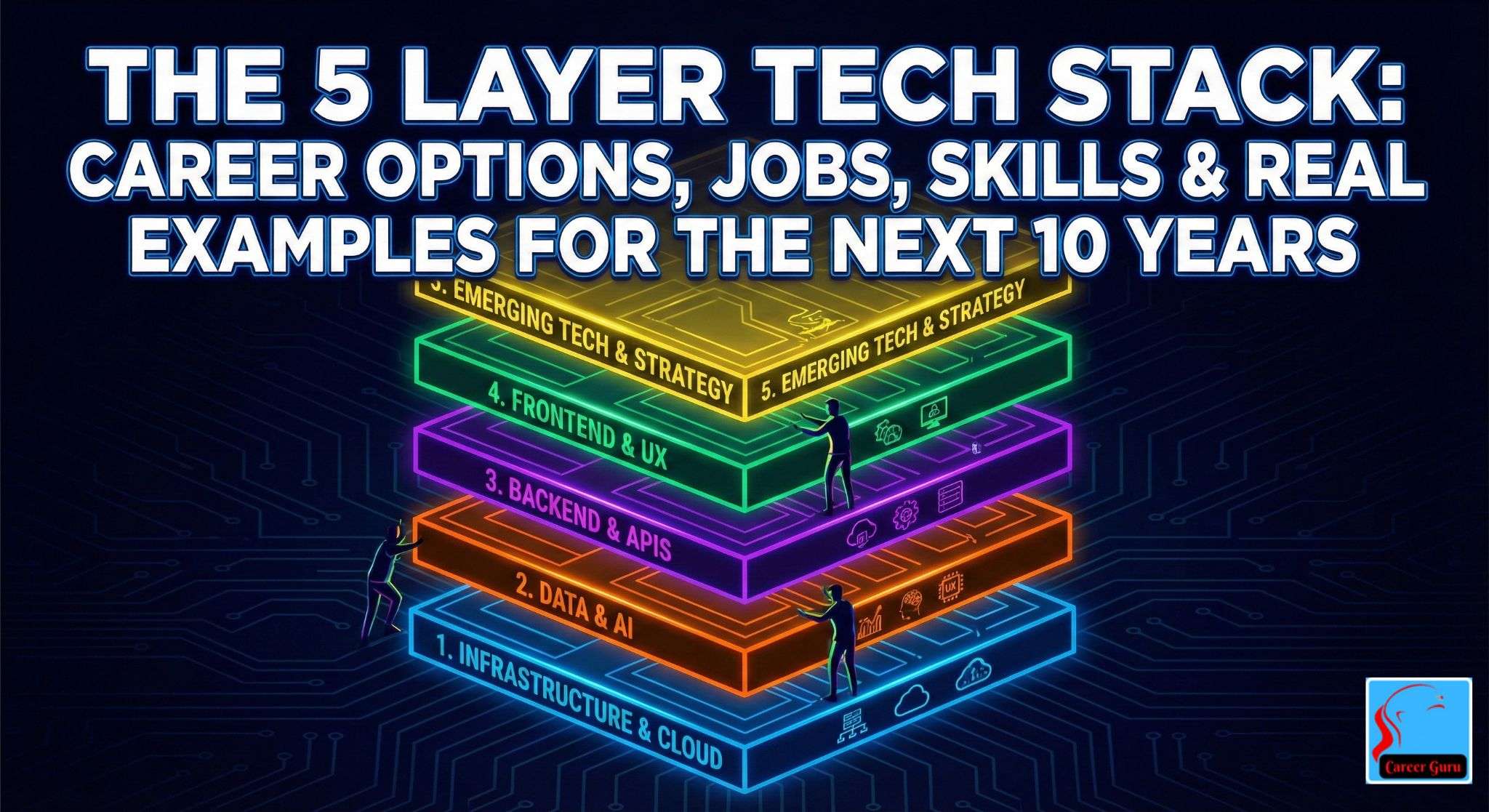
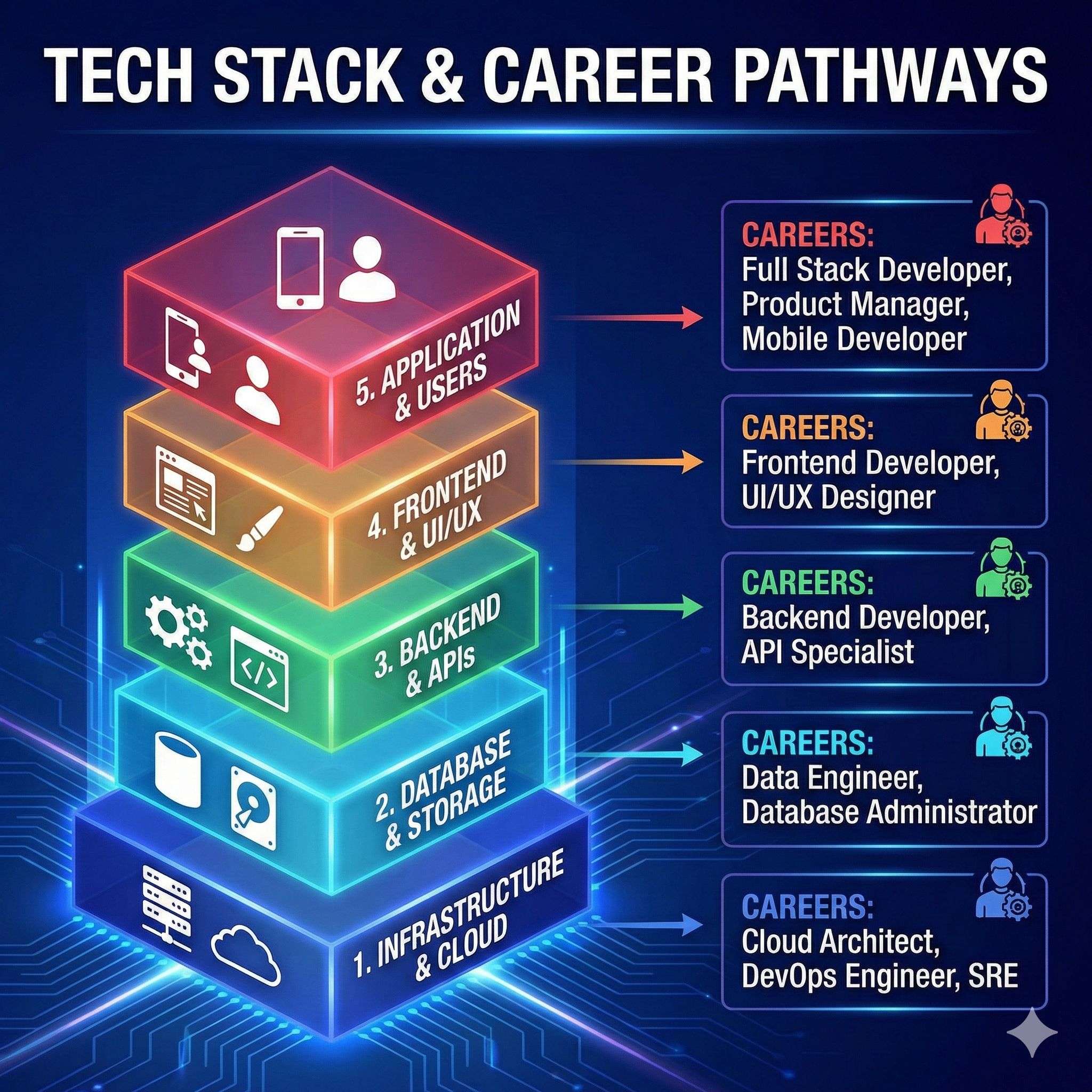
What Is the 5-Layer Tech Stack?
Think of technology like a building.
You see the top floors.
You use them every day.
But the building stands because of what is underneath.
The five layers are:
- Energy Layer
- Infrastructure Layer
- Chip Layer
- LLM or AI Intelligence Layer
- Application Layer
Each layer:
- Creates different jobs
- Needs different skills
- Attracts different types of students
Understanding this is the foundation of a strong technology career roadmap.
Layer 1: Energy Layer – The Power Behind the Digital World
What is the Energy Layer?
No electricity means:
- No internet
- No data centers
- No cloud
- No AI
This layer deals with power.
It includes:
- Power generation
- Power distribution
- Energy efficiency
- Data centre electricity management
AI data centres consume huge amounts of energy.
That is why this layer is quietly becoming very important.
Case Study: AI Data Centres in India
Large cloud companies are setting up data centres in India.
Each data centre needs:
- 24×7 power
- Backup systems
- Cooling systems
- Energy efficiency planning
This has created demand for:
- Electrical engineers
- Facilities engineers
- Energy auditors
These jobs are not flashy.
But they are stable and long-term.
Jobs in the Energy Layer
- Electrical Engineer
- Power Systems Engineer
- Renewable Energy Engineer
- Data Centre Facilities Engineer
- Energy Analyst
Who should choose this layer?
This layer is perfect if:
- You studied electrical engineering
- You are a diploma holder
- You do not enjoy coding
If you are searching for non-coding tech jobs, this layer is often ignored but powerful.
How to prepare (Simple path)
Education
- Diploma or BTech in Electrical or Power Engineering
Skills
- Power distribution basics
- Transformers and UPS
- Cooling systems
- Solar and renewable energy basics
Entry-level roles
- Junior Electrical Engineer
- Site Engineer
- Maintenance Engineer
This layer rewards patience and reliability.
Layer 2: Infrastructure Layer – Cloud, Servers & Cybersecurity
What is the infrastructure layer?
This is the backbone of technology.
It includes:
- Servers
- Networks
- Cloud platforms
- Cybersecurity
Every website, app, and AI system runs on this layer.
This is why the cloud computing career path is one of the safest today.
Real Example: A Simple Website
When you open a website:
- It runs on a server
- The server is hosted on the cloud.
- The cloud needs networking
- Security protects the data
All of this happens before the website appears.
Infrastructure professionals make this possible.
Jobs in the Infrastructure Layer
- Cloud Engineer
- System Administrator
- DevOps Engineer
- Network Engineer
- Cybersecurity Analyst
Who should choose this layer?
This layer suits:
- CS and IT students
- ECE students
- Career switchers
Many professionals start from basic IT support and grow steadily here.
Case Study: IT Support to Cloud Engineer
A graduate starts as an IT support.
Learns Linux and networking.
Moves to the system administrator.
Learns AWS.
Becomes a cloud engineer.
This journey takes 3–5 years.
But it is realistic and stable.
How to prepare
Step 1
- Learn Linux basics
Step 2
- Learn networking concepts
Step 3
- Learn cloud fundamentals
Certifications
- CCNA
- AWS Cloud Practitioner
- Azure Fundamentals
Entry roles
- Cloud Support Engineer
- Network Engineer Trainee
This layer offers strong tech stack career options.
Layer 3: Chip Layer – Semiconductors & Embedded Systems
What is the Chip Layer?
This layer builds the brains of machines.
It includes:
- Microchips
- Processors
- Embedded systems
- Semiconductor manufacturing
Countries treat this as a strategic industry.
That is why semiconductor jobs in India are gaining attention.
Example: Smartphone Hardware
Your smartphone contains:
- Multiple chips
- Sensors
- Embedded systems
Engineers design, test, and maintain these systems.
This work is deep and technical.
Jobs in the Chip Layer
- VLSI Design Engineer
- Embedded Systems Engineer
- Firmware Engineer
- Hardware Test Engineer
Who should choose this layer?
Best for:
- ECE and EEE students
- Strong electronics background
- Students who enjoy low-level systems
This is not a fast-money layer.
But it offers long-term career security.
How to prepare
Core subjects
- Digital electronics
- Microprocessors
- Communication systems
Skills
- Embedded C
- Verilog basics
- Microcontroller programming
Entry roles
- Embedded Engineer Trainee
- Hardware Test Engineer
Tech Hiring Is Back in 2025: Industry Growth Returns
How to Start a Career in AI With No Experience
Layer 4: LLM Layer – AI, Data & Intelligence
What is the LLM Layer?
This is where machines become intelligent.
It includes:
- Machine learning
- Data science
- Large language models
This layer decides how smart a system is.
It defines most AI and machine learning careers.
Simple Example: Recommendation Systems
When Netflix suggests movies:
- Data is collected
- Models analyse behaviour.
- AI predicts interest
This entire logic sits in the LLM layer.
Jobs in the LLM Layer
- Data Analyst
- Machine Learning Engineer
- AI Engineer
- Data Scientist
Students exploring an AI career after engineering usually aim here.
Case Study: From Excel to Data Analyst
A commerce graduate learns:
- Excel
- SQL
- Python
Starts as a data analyst.
Later moves to machine learning roles.
AI careers are not only for toppers.
They are for consistent learners.
How to prepare
Step 1
- Learn Python
Step 2
- Learn data analysis
- Learn basic statistics
Step 3
- Learn machine learning concepts
Tools
- Pandas
- Scikit-learn
- TensorFlow or PyTorch
Entry roles
- Data Analyst
- AI Intern
Layer 5: Application Layer – Apps, Websites & Products
What is the application layer?
This is what users see and use.
It includes:
- Websites
- Mobile apps
- SaaS platforms
- AI tools
Most visible jobs exist here.
Example: Food Delivery App
A food app includes:
- Frontend design
- Backend logic
- Payment integration
- AI recommendations
Application developers bring everything together.
Jobs in the Application Layer
- Frontend Developer
- Backend Developer
- Full-Stack Developer
- UI UX Designer
- Product Manager
This layer helps beginners understand how to choose a technology career.
How to prepare
Start with
- HTML, CSS, JavaScript
Then
- React or Angular
- Backend basics
Entry roles
- Junior Developer
- Web Developer
This layer offers faster entry but higher competition.
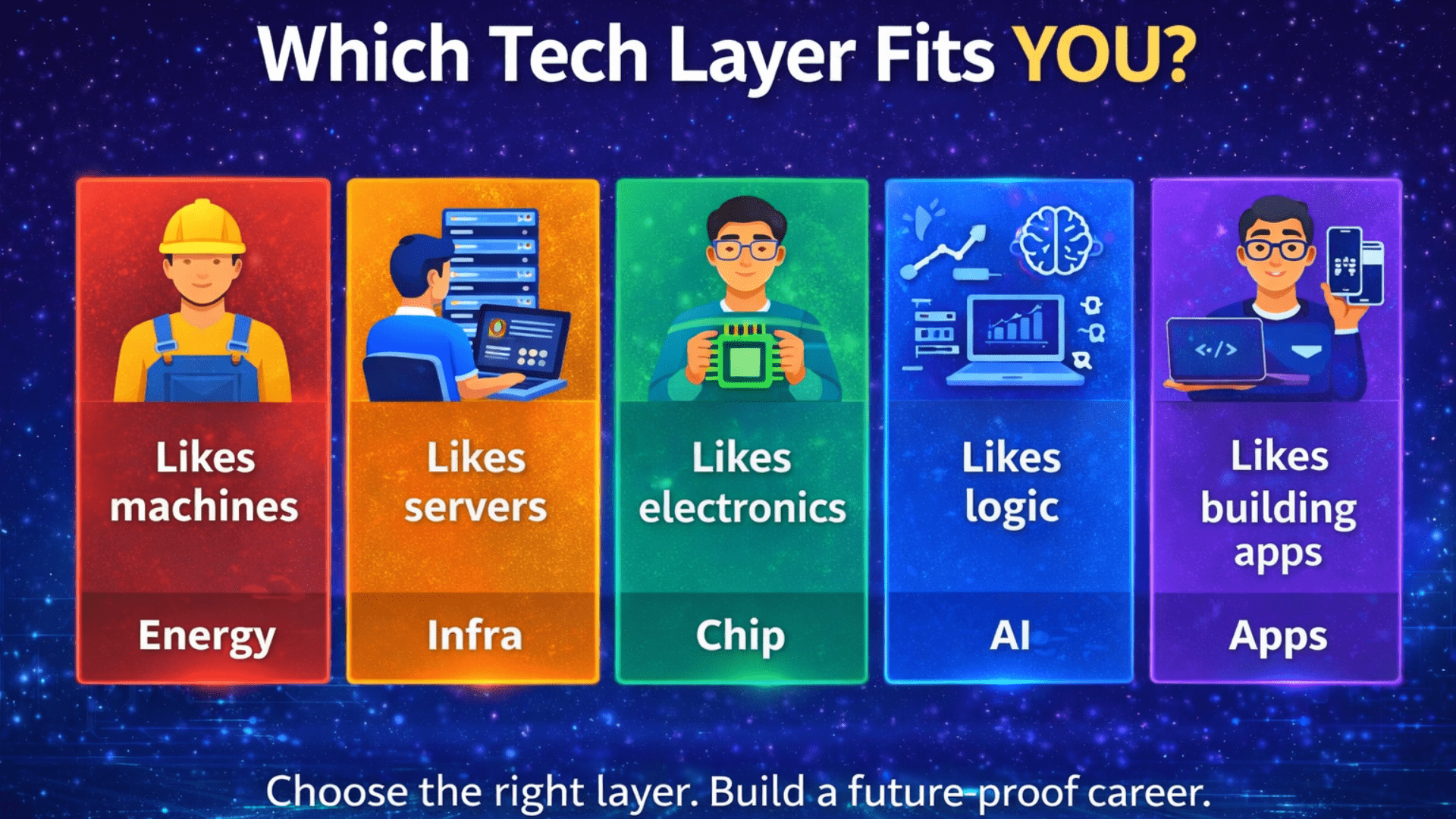
How to Choose the Right Layer (Very Important)
Ask yourself honestly:
Do I like physical systems?
→ Energy Layer
Do I like troubleshooting and servers?
→ Infrastructure Layer
Do I enjoy electronics?
→ Chip Layer
Do I enjoy logic and data?
→ LLM Layer
Do I want visible output fast?
→ Application Layer
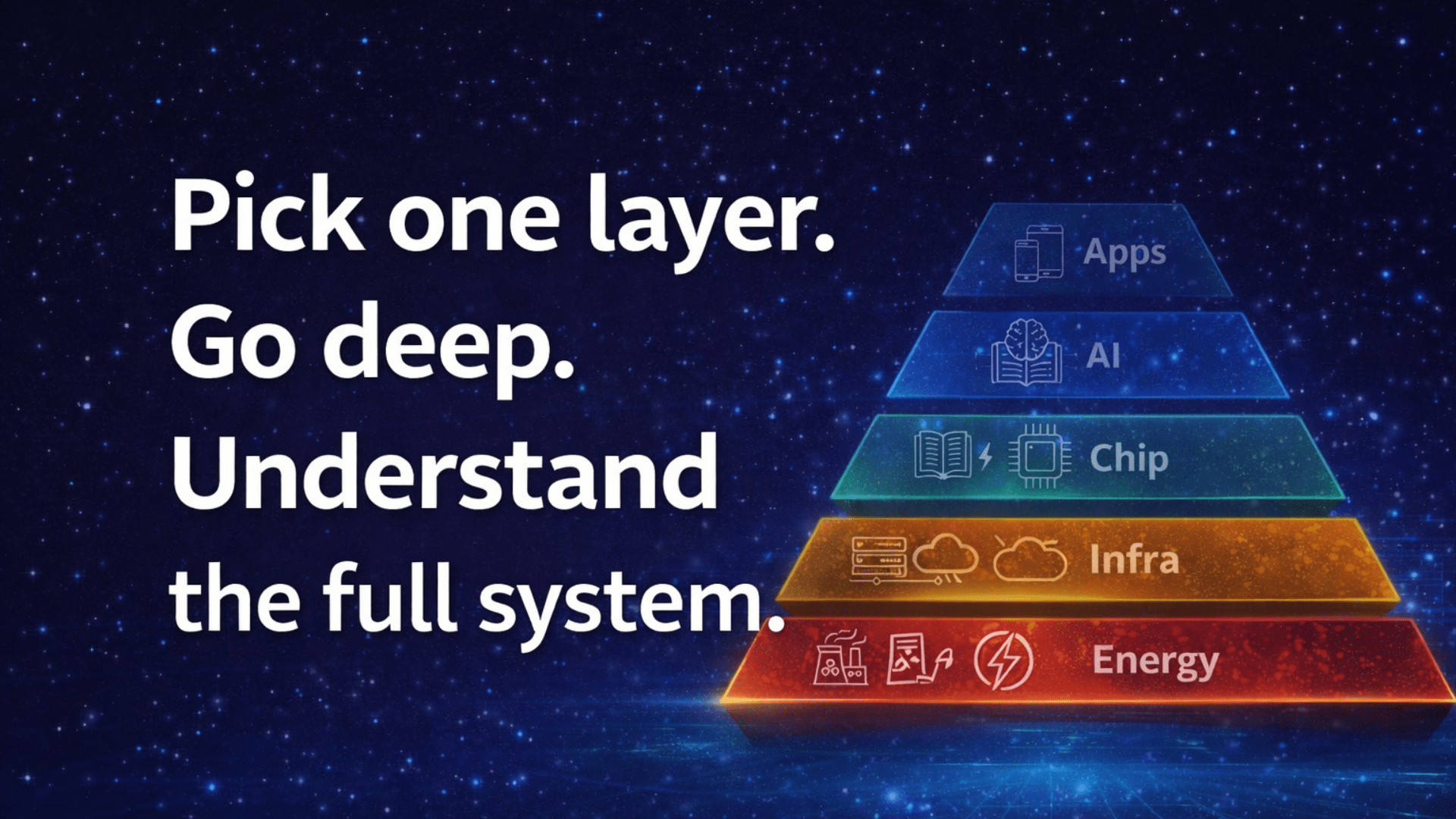
The smartest professionals master one layer deeply and understand one layer above and below.
This approach builds the best tech careers for the next 10 years.
Q 2:- Is coding mandatory everywhere?
No. Energy and Chip layers need little coding.
Q 3:- Is AI replacing developers?
AI replaces repetitive tasks. Skilled professionals remain essential.
Q 4:- Which layer is safest long-term?
Energy, infrastructure, and AI layers are the most stable.
Key Takeaways (Read This Carefully)
- Technology is layered
- One skill does not fit all
- Random courses waste years
- Choose based on interest
- Build depth, not noise
- Understand systems, not trends
Final Thought
Careers fail when decisions are rushed.
Careers grow when decisions are structured.
If you understand the 5 layer tech stack careers,
you stop guessing and start building.
This is how professionals stay relevant for decades.